Page 208 - GuideFWA
P. 208
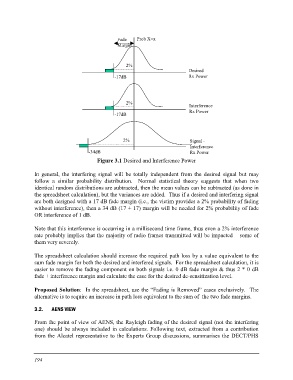
Fade Prob X=x Desired
Margin Rx Power
2%
-17dB
2% Interference
-17dB Rx Power
2% Signal -
Interference
-34dB Rx Power
Figure 3.1 Desired and Interference Power
In general, the interfering signal will be totally independent from the desired signal but may
follow a similar probability distribution. Normal statistical theory suggests that when two
identical random distributions are subtracted, then the mean values can be subtracted (as done in
the spreadsheet calculation), but the variances are added. Thus if a desired and interfering signal
are both designed with a 17 dB fade margin (i.e., the victim provides a 2% probability of fading
without interference), then a 34 dB (17 + 17) margin will be needed for 2% probability of fade
OR interference of 1 dB.
Note that this interference is occurring in a millisecond time frame, thus even a 2% interference
rate probably implies that the majority of radio frames transmitted will be impacted – some of
them very severely.
The spreadsheet calculation should increase the required path loss by a value equivalent to the
sum fade margin for both the desired and interfered signals. For the spreadsheet calculation, it is
easier to remove the fading component on both signals i.e. 0 dB fade margin & thus 2 * 0 dB
fade + interference margin and calculate the case for the desired de-sensitization level.
Proposed Solution: In the spreadsheet, use the “Fading is Removed” cases exclusively. The
alternative is to require an increase in path loss equivalent to the sum of the two fade margins.
3.2. AENS VIEW
From the point of view of AENS, the Rayleigh fading of the desired signal (not the interfering
one) should be always included in calculations. Following text, extracted from a contribution
from the Alcatel representative to the Experts Group discussions, summarises the DECT/PHS
194